Impact of Digital Technologies on Russian KIBS

The HSE Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge analysed the KIBS firms’ demand for digital technologies and the impact of their adoption on business activity. Top management survey results have shown that about 50% of the companies use big data analysis tools, and only 5.4% implement Virtual and Augmented Reality technologies. About 80% of KIBS firms applied different types of digital tools to optimise business process-es and increase competitiveness even before their massive development during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2019, as part of the ‘Monitoring of Knowledge-Intensive Business Services in Russia’ project, HSE ISSEK researchers conducted a top management survey. Respondents represented over 600 organisations engaged in such spheres as: information technologies, law, accounting, auditing, management consulting, architecture, engineering, industrial design, advertising, marketing, and market research. The sample included large, medium, and small firms operating in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk and other cities with more than one million inhabitants. Respondents were asked a set of questions regarding the demand for digital technologies and their role in the respective company’s business.
Main findings
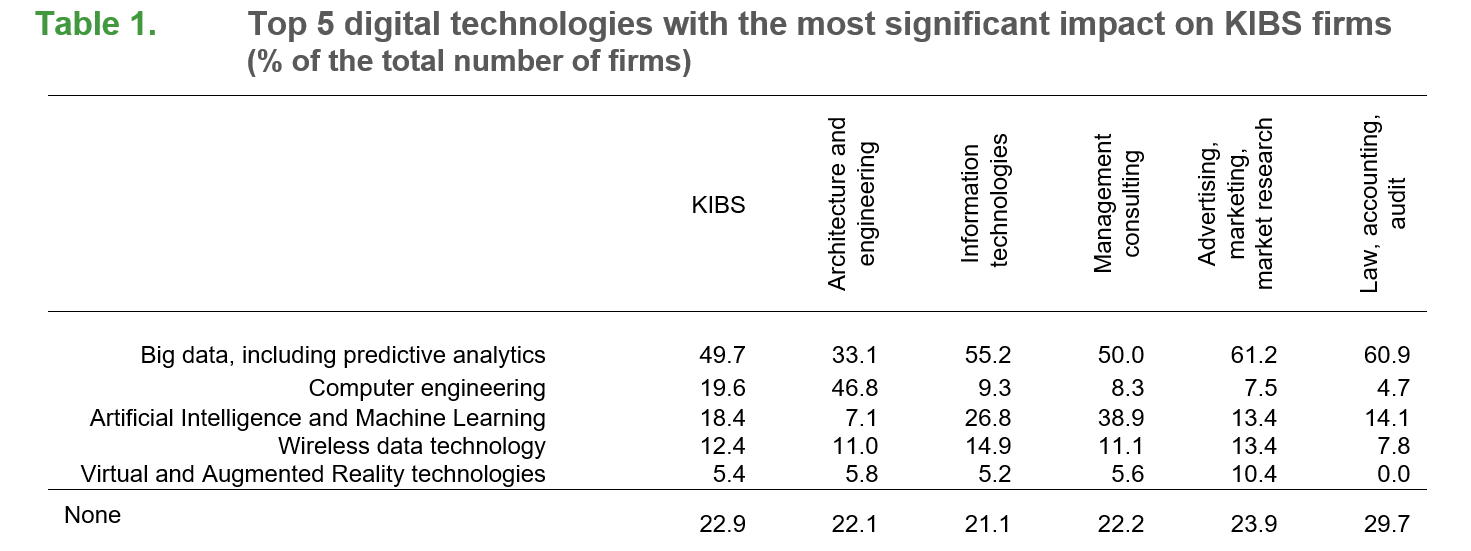
Over three quarters of KIBS firms pointed out that digital technologies played an important role in conducting business operations, transforming the range of products and services and optimising business processes. As such, 49.7% of firms especially highlighted big data technologies, including predictive analytics (Table 1). The second place was given to computer engineering technologies (19.6%), actively used in architecture and engineering (46.8%). Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies are most popular in management consulting (38.9%) and information technologies (26.8%), while wireless data transmission technologies (5G, NFC, etc.) are equally represented in all KIBS industries. Virtual and Augmented Reality technologies are more commonly used in advertising and marketing, their importance, however, remains substantially low.
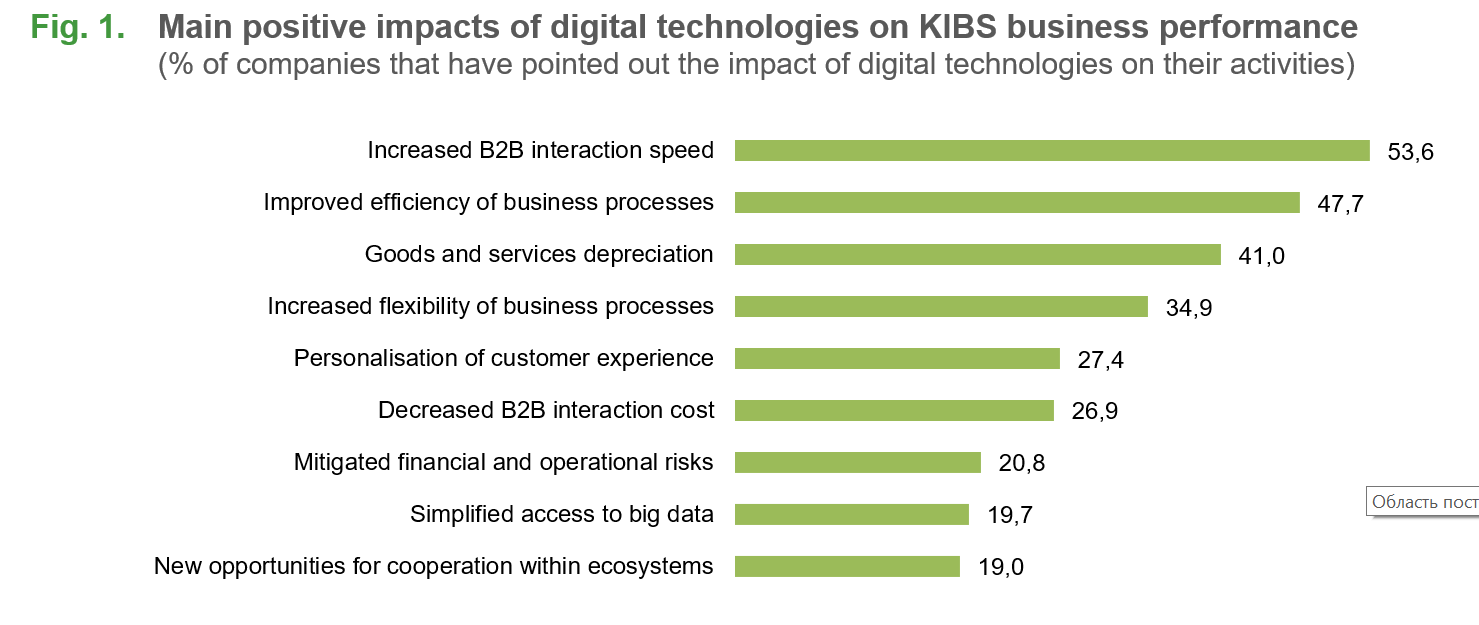
Survey results have demonstrated the positive impact of digital technologies on B2B interactions, business processes and operating activities efficiency (Fig. 1). Thus, KIBS firms are twice as likely to detect an increase in speed of interaction with client firms (53.6%), rather than a decrease in its cost (26.9%) or personalisation of customer experience (27.4%). Efficiency and flexibility of business processes increased in 47.7% and 34.9% of firms, respectively. In terms of operational activities, respondents consider goods and services depreciation to be the strongest impact (41%), and they are much less likely to mitigate financial and operational risks (20.8%) or to create new opportunities for cooperation within ecosystems (19%).
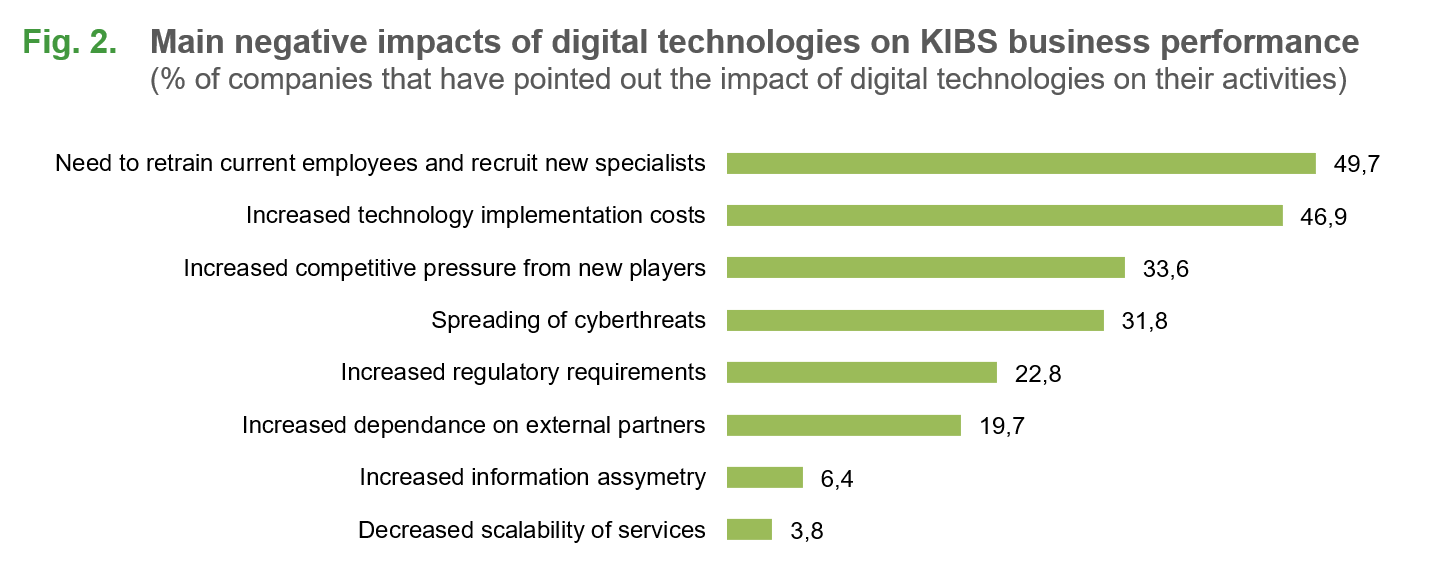
According to KIBS firms, key challenges in the sphere of digital technologies development (Fig. 2) are associated with the growing need to retrain current employees and recruit new specialists with a different skill profile (49.7%), as well as the need to seek additional funding sources for implementing these technologies (46.9%). Every third company is afraid of competitive pressure exerted by new players entering the market (primarily, IT companies) and spreading of cyberthreats, and every fifth is afraid of stringent regulatory requirements and dependence on external partners as part of the ecosystem building process.
Big data technologies and predictive analytics have the highest impact on the business performance of Russian KIBS firms. The main positive impacts of the digital technologies development are: increased speed of B2B interactions and efficiency of business processes. At the same time, the use of these technologies is associated with some challenges, such as raising additional funds for their implementation and the need for human capital development.
Sources: HSE ISSEK calculations based on Monitoring of the State and Dynamics of the KIBS Sector in Russia data; results of the ‘Study of the activity of innovation process actors: strategies, network interactions, institutions’ project carried out as part of the HSE Programme of Fundamental Studies.
Authors: Nikolay Chichkanov & Veronika Belousova
Translators: Mariam Kordzadze & Zhaklin Krayushkina
Editor: Mariya Rukhalenko