Russians’ Digital Practices During Lockdown

The HSE Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge has released the results of its survey on digital practices in 2020, which illustrate the changes in how people have mastered new formats to solve routine tasks.
Key Outcomes
During the lockdown, 76% of the respondents started using digital tools for routine tasks more often. Half of the respondents (49%) downloaded new apps and software. 34% mastered a new skill, and 48% planned to do so in the near future.
Despite the generally active use of the internet, the respondents’ preferences in tools to solve different tasks vary greatly. The most digitalized tasks are practices such as information search, use of public services (including related services such as utilities payments), online trade (goods and services), and entertainment (music, films, etc). Digitalization indices in these fields exceed 70 out of 100 (Fig. 1). The reason for this is the strength of relevant services and platforms. That said, none of the popular digital practices has completely transitioned to an online format.
Figure 1. Digitalization of social practices
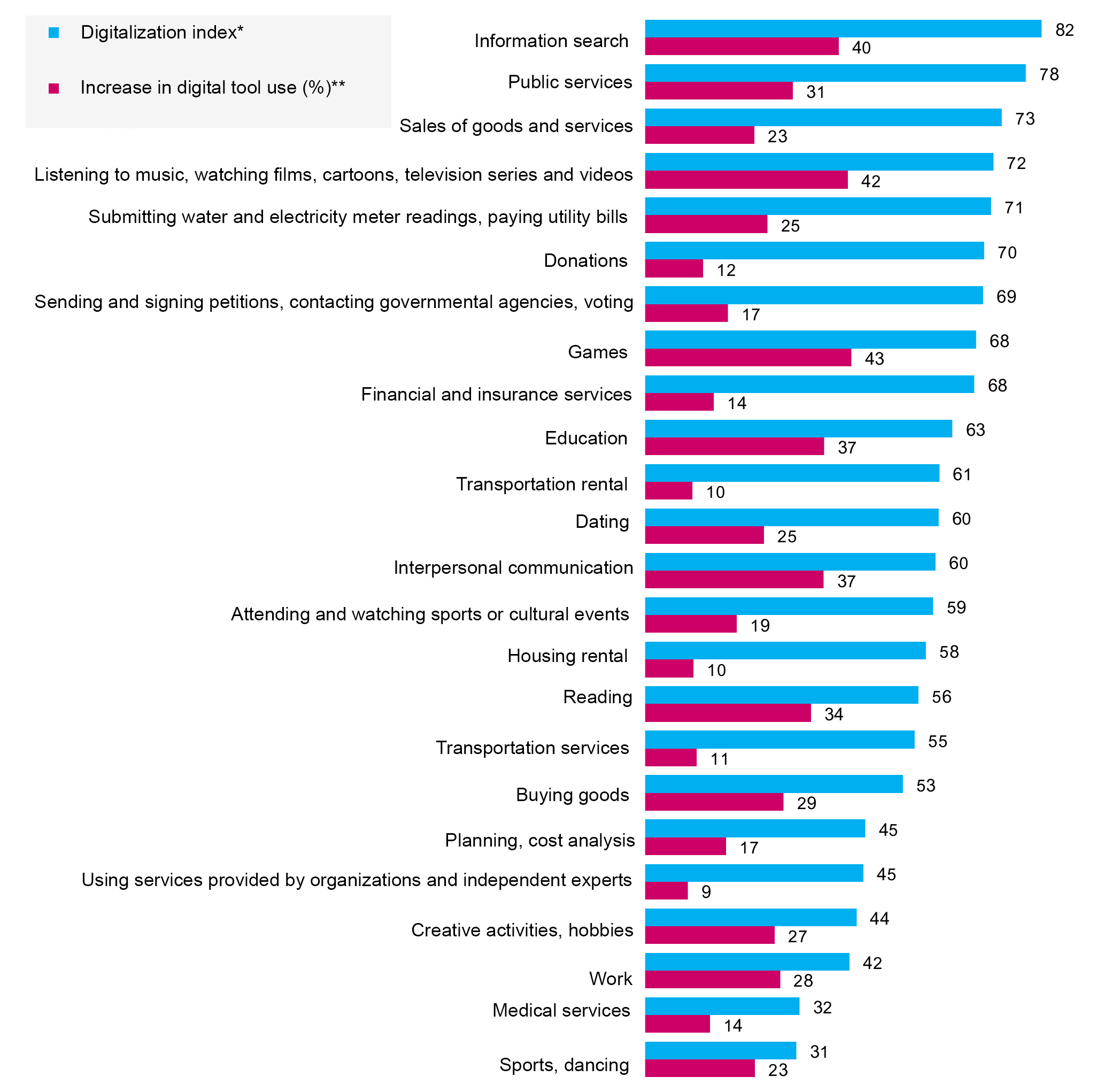
* Digitalization index was calculated on the basis of a survey on internet use in different social practices according to the formula: (0*(offline only) + 25* (offline more often) + 50* (offline and online in equal shares) + 75* (online more often) + 100* (online only)) / 100% - (didn’t do it at all) - (no answer). The minimum value of the index is 0 and means that no digital tools are used for this everyday task; the maximum value is 100 and means that only digital tools are used. Values around 50 indicate a balance between online and offline services.
** Increase in digital tool use is the proportion of users who started using online services during the lockdown more often in the total number of respondents who use this practice.
High levels of digitalization can also be seen in activities such as contacting government agencies and voting, games, educational activities, accessing financial and insurance services, transportation rental, and communications (digitalization indices vary from 60 to 69).
In other fields, digitalization has not yet led to a considerable decrease in the role of non-digital tools. For example, 74% of respondents have bought goods or services online over the last 12 months, but the digitalization index is 53, which means that the respondents buy equally online and in traditional stores.
The lowest popularity of digital services is in medical services and sports/dancing (digitalization indices are 32 and 31, respectively). Work-related use shows a low level of digitalization (42): while almost half of the respondents (44%) use the internet at work, more respondents perform most of their work responsibilities on-site. A vast majority (70%) of the employed respondents do not work from home.
The pandemic facilitated growing internet use in certain social practices. Forced digitalization has been most vivid in the consumption of information and entertainment content, the use of public and educational services, and interpersonal communication. The intensity of internet use in these types of activities grew by 37-43% during the lockdown. This means that over one-third of consumers of these services started using them more often during the lockdown.
The study shows considerable changes in users’ lifestyles that have been triggered by the pandemic. Some digital practices have not only seen increased demand during mandatory self-isolation but have also demonstrated the capability to replace traditional patterns. The active use of digital services and devices has motivated people to improve relevant skills, which may lead to growth in digital literacy among the population in the near future.
Sources: HSE ISSEK calculations based on the ‘Study of factors of population integration in the digital economy and the effects of the pandemic on the intensity of digital technology use in the society,’ which was carried out in line with the topical plan of research as part of the HSE University state assignment.
The article prepared by Valentina Polyakova, Anastasia Nesterenko and Konstantin Fursov
Translation by HSE.ru
Valentina Polyakova
Research Fellow, Unit for Analysis of R&D Performance
Konstantin Fursov
Deputy Director, Centre for Statistics and Monitoring of S&T and Innovation